Last updated:
Table of contents
- Located
- Process
- Preconditions to start
- Rules
- Timetable and phase selection
- TAB view
- Reference train content during carry-forward
- System validations
1. Located
The carry-forward function is located on the Reference Train view, in the bulk options at the “More” menu. To access the carry forward option, expand the arrow on the “more” menu
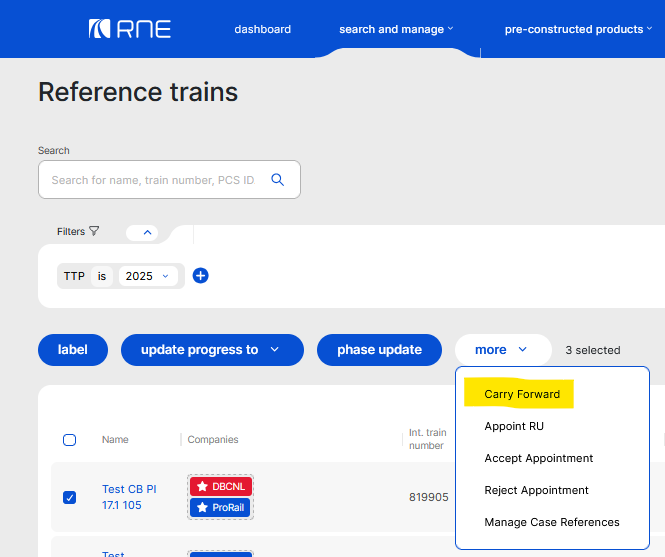
2. Process
On the reference train view, users can apply filter conditions to search for the reference train or trains that they wish to carry forward to the next timetable period. For example, in the year 2025, reference train creation is opened for TTP2025 and TTP2026. If a reference train created in TTP2025 would be available to carry forward for TTP2026.
The carry-forward process is the following:
- Select train/s
- Start carry forward
- System validation check in the backround
- Carry-forward result
- Successful carry-forward
- In case of unsuccessful carry-forward, users should check the reason for the errors
2.1 Supported
- New path request (NPR)
- Late Path request (LPR)
- Adhoc path request (adhoc)
- Partial process
- For a partial process, the carry forward is possible, but only from requests
2.2 Not supported
For an adhoc partial process, the carry forward is not supported.
3. Precondition to start
The following preconditions exist:
- Users have to select one or more reference trains from the list of available reference trains to display the bulk options
- The next timetable period is already available and open for creating reference trains
4. Rules
- All involved applicants (a minimum of one territory) can carry forward the reference train. If the responsible applicant carries the train forward, they will become the LA in the newly created reference train by default
- A reference train can be carried forward only to the next timetable period in order
- When the selected reference train is not in a neighbouring timetable period, the carry-forward option is not available. For example, if the reference train is selected in the TTP2022, the carry-forward option is not available, and users are unable to carry forward their selected RTs from TTP2022 to TTP2026
- If there are more timetable periods available and open for reference train creation (rare, but can happen), then the latter timetable period is applied as the target TTP
- A reference train can be carried forward as many times as the user wants. There is no limitation.
- The reference train will always be carried forward to the Open phase.
5. Timetable and phase selection
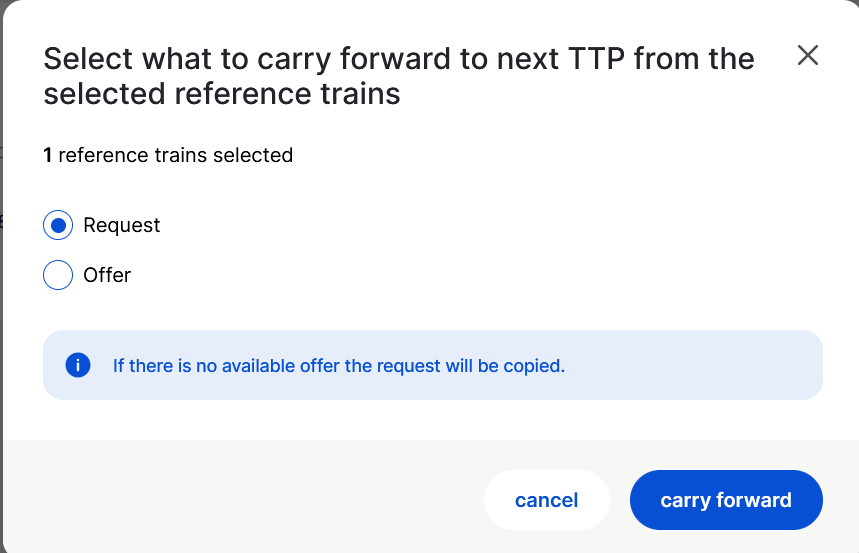
After the carry-forward menu opens, users can select which timetable they wish to carry forward: Request or Offer, if both exist, for carry forward.
The default value on the pop-up window is always the Request.
If there are no available offers in the selected reference train, then the Request will be copied by default
6. TAB view
The view works as any other bulk promotion tab view. Only those tabs are shown where there is something to be displayed.
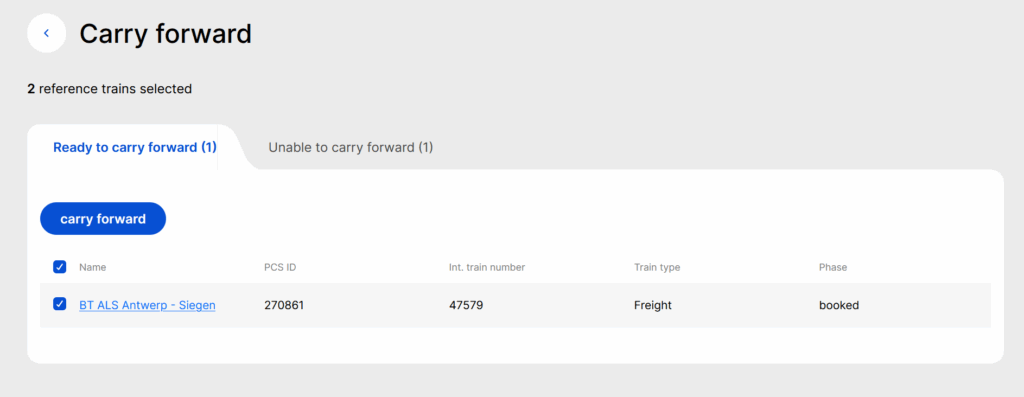
When the user clicks the carry forward option, a two-tab view may be opened:
- The first tab contains the trains where the user is allowed to perform carry forward
- The second tab contains trains where it’s not possible to perform the carry-forward
- That can happen for several reasons:
- User does not have the right permissions
- The timetable period is not open
- That can happen for several reasons:
If users do not have sufficient access or the carry-forward cannot be used for the reference train, the following message will be shown
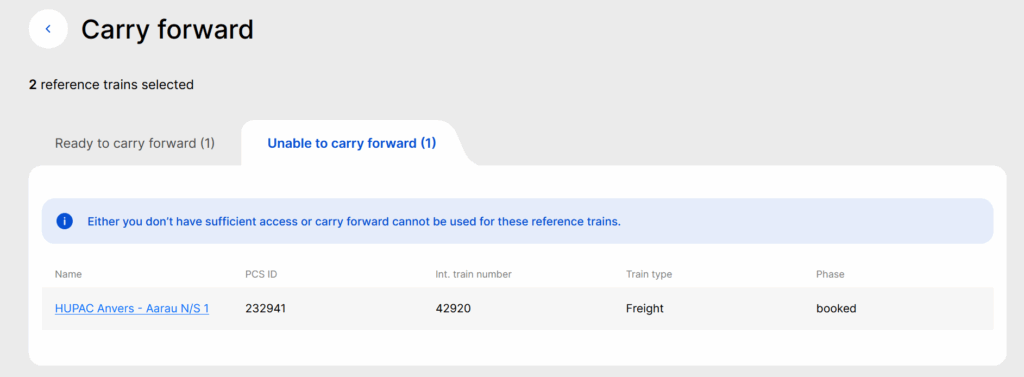
Selecting the carry forward option opens a new view, where the following reference train details are displayed
A blue information toast message is displayed when the carry-forward process is executed by the user

When the carry-forward is finished, an email notification is sent to the user.
7. Reference train content during carry-forward
Not every content is copied to the newly created reference trains. The following contents will be kept, not kept or newly configured:
- Kept
- Reference train name
- International train number
- Train type
- Train composition
- Involved agencies, agencies in general, leading roles
- Request tab: created either based on the request or the offer. This includes: territories, timetable information, NSPs, train parameters, and calendar
- Not kept
- Comments
- PaP references. If the feature is applied on a freight train with PaPs, the carry forward would work, but it would make a tailor-made copy of the train for the next timetable period. All PaPs and their references, just like the RFCs as reference train participants, are removed.
- Newly configured
- Reference train phase: Open
- Path request progress status is reset to “not yet started” (blue)
- (blue)Process type: based on the current date and the timetable period
- History
- Validity period
- IDs: IDs are generated automatically in this case. The behaviour is the same as if the user chooses the automatic ID generation during the reference train creation process.
8. System validations
After the user clicks on the “carry forward” button, the process starts, and the system validates the reference train data with the reference data that is configured in PCS exists and is valid:
- Locations are valid
- Loco types exist
- Activity types exist
- NSPs exist
- Common mandatory parameters exist
- Code list update
The general rule is that if any of the parameters that do not exist in the target TTP are dropped.
See each above points below in detail.
8.1 Locations
If the location is valid, it will be copied over as a valid location.
It can happen that a location is not valid anymore. In this case, the location is still copied, but marked on the Graphical User Interface (GUI) that is invalid in read-only and editing mode.
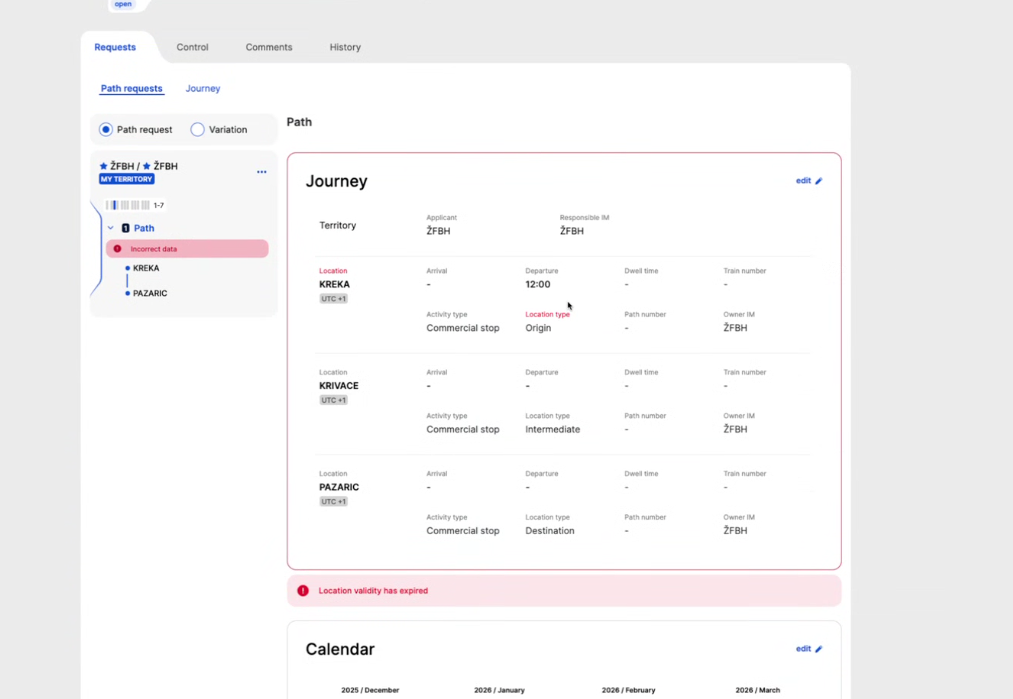
The same blocker type of error as for the empty location is applied here. Users are blocked from continuing to the next step in edit mode until a valid location is provided.
Also, an error is shown below the journey section: “Location validity has expired”.
8.2 Loco types
If the loco type is valid will be copied over as a valid loco type.
If the loco type is invalid, it is still copied, but marked on the Graphical User Interface (GUI) that is invalid in read-only and editing mode. Users can continue to the next step, but they are blocked from setting the green light until a valid loco type is provided.
8.3 Activity types
If the activity type is valid, it will be copied over as a valid activity type.
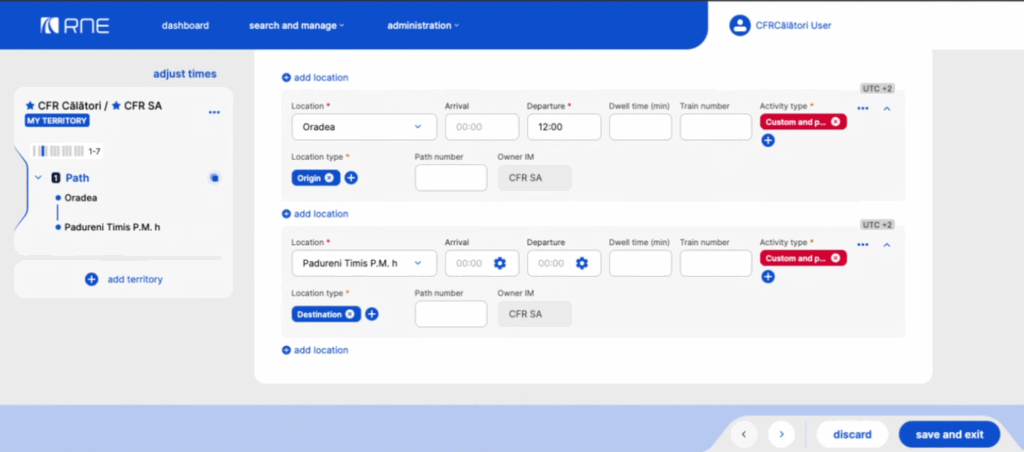
The same error handling is applied for activity types as for the invalid loco types. If the activity type is invalid, it is still copied, but marked on the Graphical User Interface (GUI) that is invalid in read-only and editing mode. Users can continue to the next step, but they are blocked from setting the green light until a valid loco type is provided.
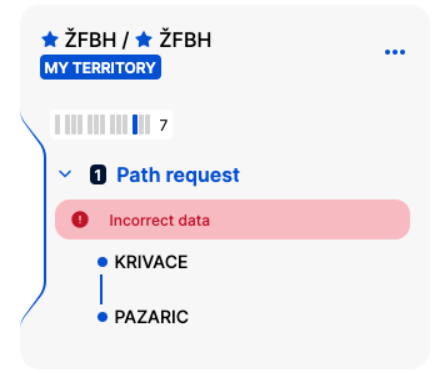
In the below example, the activity type is invalid, the badge is shown in the red backround:
8.4 NSPs
NSP form is re-initialised, and the fields/values in the new train and commonly available fields/values are copied over to the newly created train.
8.5 Common mandatory parameters
If the common mandatory parameter is detected as mandatory to fill, it will be copied over as a mandatory field.
If the common mandatory parameter is detected as optional, it will be copied over as an optional field.
When by default optional field was turned into mandatory, but the validity ends, it’s simply marked as optional again in the newly created train.
8.6 Calendar
The calendar shall be copied bit by bit (day to day) to the next timetable period. It means if the timetable period starts on a Sunday, then the first Sunday of the source calendar of the TTP where users would like to carry forward “from” should go to the first Sunday of the target calendar where users would like to carry forward “to”, and so on.
There is an edge case when the target calendar is longer than the source:
- It can be either a leap year (29th of February)
- Just simply longer because the target calendar has 53 weeks instead of 52
The same running days are copied over from the source TTP to the target TTP.
8.7 Validity Exparies
Any of the parameters that are expired and invalid in the target TTP, the following messages are shown in the newly created reference train: